Coagulation Disorders in Chronic Liver Disease
Abstract
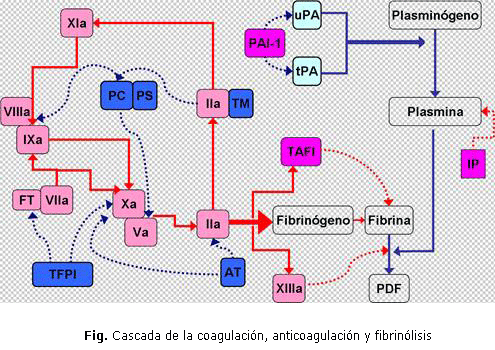
Normal haemostasis performs based on a complex balance between procoagulant, anticoagulant mechanisms and the fibrinolytic system, in which the liver exerts an important role. A review was performed aimed at examining aspects in relation with the hemostatic alterations in patients with chronic liver disease. A bibliographical review was done to accomplish that purpose in Pubmed, EBSCO, Medline, and Hinari database. Platelet quantitative and qualitative abnormalities and diminished synthesis of clotting factors were approached, as well as dysfibrinogenemia, fibrinolysis disorders, vitamin K deficiency, and a state compatible with disseminated intravascular coagulation. The following conclusions were made: the hemostatic disorders in the patient with cirrhosis are related to an advanced state of the disease, with clinical consequences which are in a wide spectrum from bleeding tendency to thrombosis, and that the standard coagulation tests do not appropriately reflect these phenomena. Nevertheless, recent advances in analytical techniques for the diagnosis of these abnormalities constitute promising tools for their proper identification in the clinical context.
Keywords: hemostasis, chronic liver disease, blood Coagulation, blood coagulation tests.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
ACCESS AND DISTRIBUTION POLICY
All published articles are open access contributions, which are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 License which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the primary source of publication is properly cited.



