Neurotoxoplasmosis Diagnosed by Computed Tomography in a Patient with AIDS
Abstract
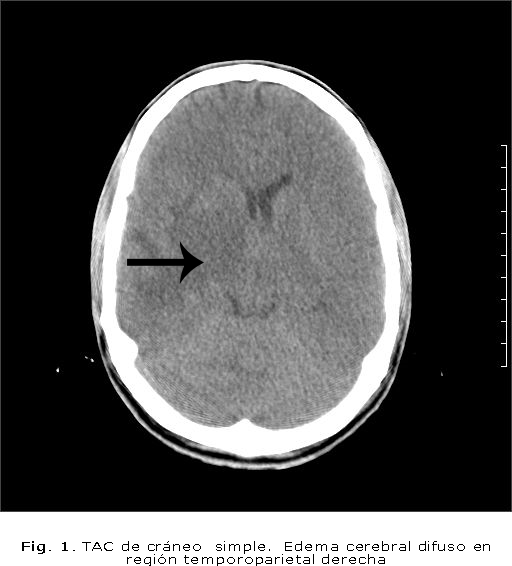
The neurotoxoplasmosis (NTX) is one of the most common opportunistic infections in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus and is presented with diverse clinical manifestations in immunocompromised host; it is also considered an AIDS-defining illness in approximately 5 % of patients infected with this virus. A patient of 24 years with a history of HIV, admitted with fever, severe headache and vomiting was presented. The toxoplasma test was positive. Computed tomography (CT) after intravenous administration that showed the presence of two nodular ring enhancement isodense with a 16 x 12 mm right parietal and a 26 x 22 mm left parietal, concluding as a cerebral toxoplasmosis. Neuroimaging techniques are valuable for diagnosis; the most used are CT and magnetic resonance. The differential diagnosis should be made in these cases with lymphoma and primary central nervous system tumors, brain metastases and stroke. The prognosis of patients with this condition depends on early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Keywords: neurotoxoplasmosis, AIDS, computerized axial tomography.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
ACCESS AND DISTRIBUTION POLICY
All published articles are open access contributions, which are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 License which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided that the primary source of publication is properly cited.



