Beyond the Definition of Metabolic Syndrome: Uric Acid, High Sensitivity C Reactive Protein and Global Cardiovascular Risk
Resumen
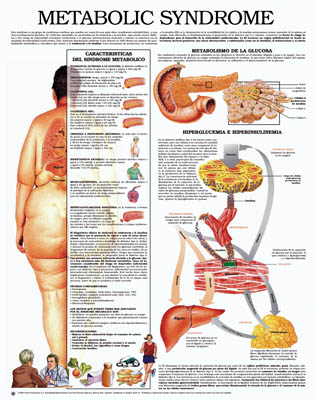
Introduction: the metabolic syndrome is becoming one of the main problems in public health.
Objective: to evaluate the relation between metabolic syndrome and uric acid, high sensitivity c reactive protein, total cardiovascular risk and cardiovascular events. Methods: a study of cases controls nested in a dynamic cohort was carried out in Velasco Teaching Polyclinic from 2010 to 2015, the cases were 67 patients that developed metabolic syndrome during the period and the control group were 67 patients matched by sex and age ± 5 years. The participants underwent a physical examination, anthropometry, laboratory test; all the study participants were under continuous surveillance during 4.5 years for development of cardiovascular events.
Results: the waist circumference (p = 0.000), systolic (p= 0.0042) and diastolic blood pressure (p= 0.0298), high sensitivity c reactive protein (p= 0.0039) and uric acid (p= 0.0283) were significantly associate in both groups. The body mass index was higher than 30 kg/m2 (OR 7.54; CI95%:3.35-16.9), LDL cholesterol greater than 4.16 mmol/l (OR 3.49; CI 95%:1.58-7.70) and hs CRP higher than 1 mg/dl (OR 3.59; CI 95%:1.51-8.51) showed statistically significant differences according to groups of studies. Global cardiovascular risk greater 20%, it was 3.84 times higher in the group with metabolic syndrome (CI 95%:1.67-8.82), 13.4% of the patients with metabolic syndrome developed a cardiovascular event during the period in comparison with the 2.9% in the group without metabolic syndrome (OR= 5.04; CI 95%: 1.04-24.3).
Conclusions: metabolic syndrome was significantly associated with mean level of uric acid, high sensitivity c reactive protein, total cardiovascular risk and cardiovascular events.
Keywords: metabolic syndrome, high sensitivity c reactive protein, uric acid, total cardiovascular risk, primary health care
Descargas
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Política de acceso y distribuciónEl total de los artículos publicados son contribuciones de acceso abierto, que se distribuyen según los términos de la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución–NoComercial 4.0 que permite el uso, distribución y reproducción no comerciales y sin restricciones en cualquier medio, siempre que sea debidamente citada la fuente primaria de publicación.



